React Native Firebase
Welcome to React Native Firebase! To get started, you must first setup a Firebase project and install the "app" module.
React Native Firebase is the officially recommended collection of packages that brings React Native support for all Firebase services on both Android and iOS apps.
React Native Firebase fully supports React Native apps built using React Native CLI or using Expo.
Prerequisites
Before getting started, the documentation assumes you are able to create a project with React Native and that you have an active Firebase project. If you do not meet these prerequisites, follow the links below:
Additionally, current versions of firebase-ios-sdk have a minimum Xcode requirement of 15.2, which implies a minimum macOS version of 13.5 (macOS Ventura).
Installation for React Native CLI projects
Installing React Native Firebase to a RN CLI project requires a few steps; installing the NPM module, adding the Firebase config files & rebuilding your application.
For projects using Expo, see this section below.
1. Install via NPM
Install the React Native Firebase "app" module to the root of your React Native project with NPM or Yarn:
# Using npm
npm install --save @react-native-firebase/app
# Using Yarn
yarn add @react-native-firebase/app
The @react-native-firebase/app module must be installed before using any other Firebase service.
2. React Native CLI - Android Setup
To allow the Android app to securely connect to your Firebase project, a configuration file must be downloaded and added to your project.
Generating Android credentials
On the Firebase console, add a new Android application and enter your projects details. The "Android package name" must match your
local projects package name which can be found inside of the namespace field in /android/app/build.gradle, or in the
manifest tag within the /android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml file within your project for projects using android gradle plugin v7 and below
The debug signing certificate is optional to use Firebase with your app, but is required for Dynamic Links, Invites and Phone Authentication. To generate a certificate run
cd android && ./gradlew signingReport. This generates two variant keys. You have to copy both 'SHA1' and 'SHA-256' keys that belong to the 'debugAndroidTest' variant key option. Then, you can add those keys to the 'SHA certificate fingerprints' on your app in Firebase console.
Download the google-services.json file and place it inside of your project at the following location: /android/app/google-services.json.
Configure Firebase with Android credentials
To allow Firebase on Android to use the credentials, the google-services plugin must be enabled on the project. This requires modification to two
files in the Android directory.
First, add the google-services plugin as a dependency inside of your /android/build.gradle file:
buildscript {
dependencies {
// ... other dependencies
// NOTE: if you are on react-native 0.71 or below, you must not update
// the google-services plugin past version 4.3.15 as it requires gradle >= 7.3.0
classpath 'com.google.gms:google-services:4.4.2'
// Add me --- /\
}
}
Lastly, execute the plugin by adding the following to your /android/app/build.gradle file:
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
apply plugin: 'com.google.gms.google-services' // <- Add this line
3. React Native CLI - iOS Setup
To allow the iOS app to securely connect to your Firebase project, a configuration file must be downloaded and added to your project, and you must enable frameworks in CocoaPods
Generating iOS credentials
On the Firebase console, add a new iOS application and enter your projects details. The "iOS bundle ID" must match your local project bundle ID. The bundle ID can be found within the "General" tab when opening the project with Xcode.
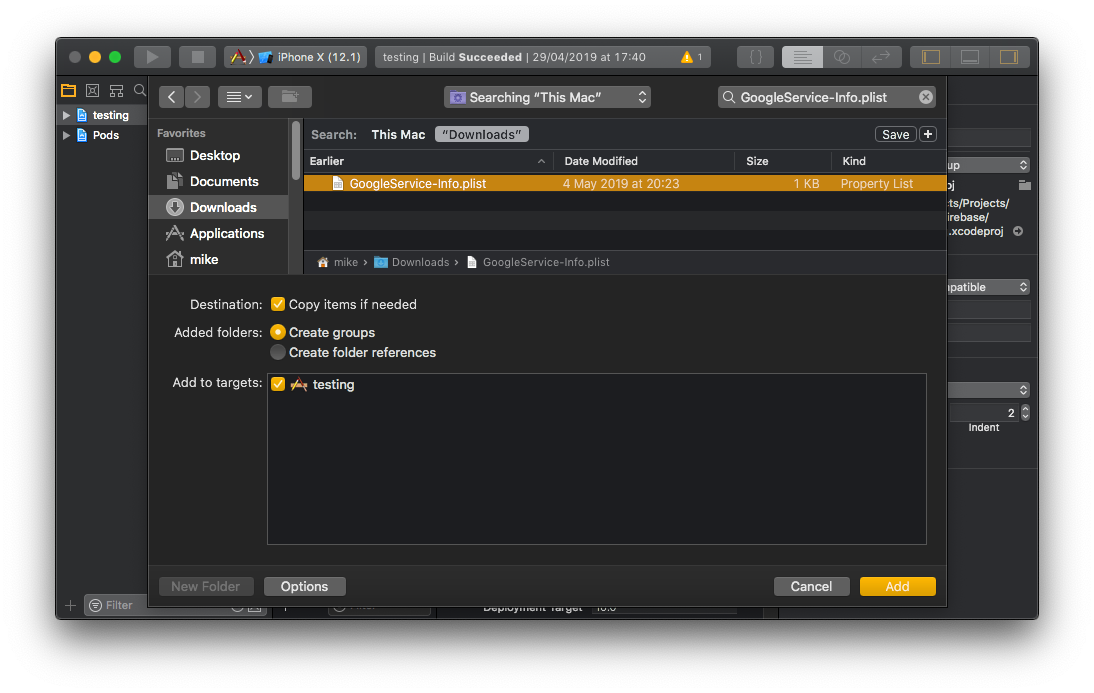
Download the GoogleService-Info.plist file.
Using Xcode, open the projects /ios/{projectName}.xcodeproj file (or /ios/{projectName}.xcworkspace if using Pods).
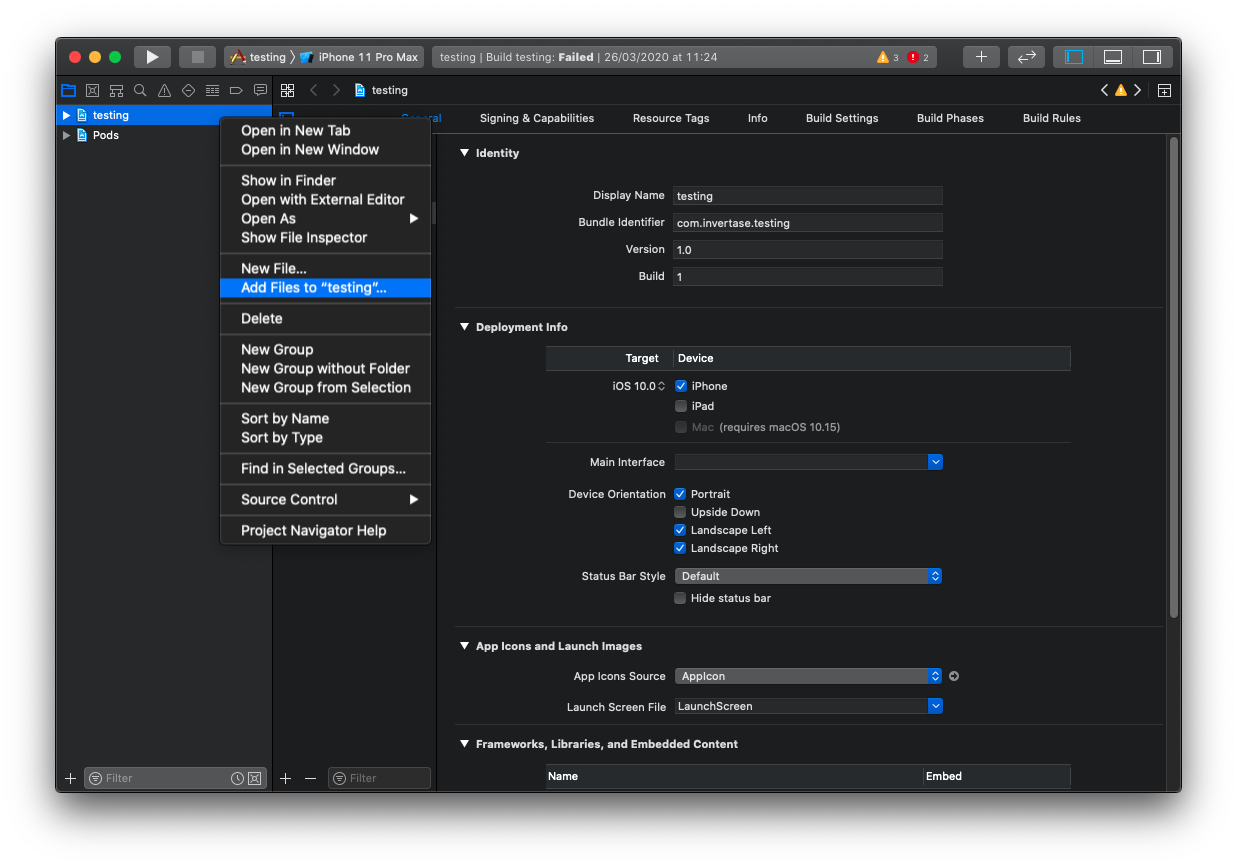
Right click on the project name and "Add files" to the project, as demonstrated below:
Select the downloaded GoogleService-Info.plist file from your computer, and ensure the "Copy items if needed" checkbox is enabled.
Configure Firebase with iOS credentials
To allow Firebase on iOS to use the credentials, the Firebase iOS SDK must be configured during the bootstrap phase of your application.
To do this, open your /ios/{projectName}/AppDelegate.mm file (or AppDelegate.m if on older react-native), and add the following:
At the top of the file, import the Firebase SDK right after '#import "AppDelegate.h"':
#import <Firebase.h>
Within your existing didFinishLaunchingWithOptions method, add the following to the top of the method:
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
// Add me --- \/
[FIRApp configure];
// Add me --- /\
// ...
}
Altering CocoaPods to use frameworks
Beginning with firebase-ios-sdk v9+ (react-native-firebase v15+) you must tell CocoaPods to use frameworks.
Open the file ./ios/Podfile and add this line inside your targets (right before the use_react_native line in current react-native releases that calls the react native Podfile function to get the native modules config):
use_frameworks! :linkage => :static
To use Static Frameworks on iOS, you also need to manually enable this for the project with the following global to your /ios/Podfile file:
# right after `use_frameworks! :linkage => :static`
$RNFirebaseAsStaticFramework = true
Notes: React-Native-Firebase uses
use_frameworks, which has compatibility issues with Flipper & Fabric.Flipper:
use_frameworksis not compatible with Flipper. You must disable Flipper by commenting out the:flipper_configurationline in your Podfile. Flipper is deprecated in the react-native community and this will not be fixed - Flipper and react-native-firebase will never work together on iOS.New Architecture: Fabric is partially compatible with
use_frameworks!. If you enable the bridged / compatibility mode, react-native-firebase will compile correctly and be usable.
4. Autolinking & rebuilding
Once the above steps have been completed, the React Native Firebase library must be linked to your project and your application needs to be rebuilt.
Users on React Native 0.60+ automatically have access to "autolinking", requiring no further manual installation steps. To automatically link the package, rebuild your project:
# Android apps
npx react-native run-android
# iOS apps
cd ios/
pod install --repo-update
cd ..
npx react-native run-ios
Once successfully linked and rebuilt, your application will be connected to Firebase using the @react-native-firebase/app module. This module does not provide much functionality, therefore to use other Firebase services, each of the modules for the individual Firebase services need installing separately.
Manual Linking
If you're using an older version of React Native without autolinking support, or wish to integrate into an existing project, you can follow the manual installation steps for iOS and Android.
Expo
Integration with Expo is possible when using a development build. You can configure the project via config plugins or manually configure the native projects yourself (the "bare workflow").
NOTE: React Native Firebase cannot be used in the pre-compiled Expo Go app because React Native Firebase uses native code that is not compiled into Expo Go.
Your Expo project
To create a new Expo project, see the Get started guide in Expo documentation.
Install React Native Firebase modules
To install React Native Firebase's base app module, use the command npx expo install @react-native-firebase/app.
Similarly you can install other React Native Firebase modules such as for Authentication and Crashlytics: npx expo install @react-native-firebase/auth @react-native-firebase/crashlytics.
Configure React Native Firebase modules
The recommended approach to configure React Native Firebase is to use Expo Config Plugins. You will add React Native Firebase modules to the plugins array of your app.json or app.config.js. See the note below to determine which modules require Config Plugin configurations.
If you are instead manually adjusting your Android and iOS projects (this is not recommended), follow the same instructions as React Native CLI projects.
To enable Firebase on the native Android and iOS platforms, create and download Service Account files for each platform from your Firebase project. Then provide paths to the downloaded google-services.json and GoogleService-Info.plist files in the following app.json fields: expo.android.googleServicesFile and expo.ios.googleServicesFile. See the example configuration below.
For iOS only, since firebase-ios-sdk requires use_frameworks then you want to configure expo-build-properties app.json by adding "useFrameworks": "static". See the example configuration below.
The following is an example app.json to enable the React Native Firebase modules App, Auth and Crashlytics, that specifies the Service Account files for both mobile platforms, and that sets the application ID to the example value of com.mycorp.myapp (change to match your own):
{
"expo": {
"android": {
"googleServicesFile": "./google-services.json",
"package": "com.mycorp.myapp"
},
"ios": {
"googleServicesFile": "./GoogleService-Info.plist",
"bundleIdentifier": "com.mycorp.myapp"
},
"plugins": [
"@react-native-firebase/app",
"@react-native-firebase/auth",
"@react-native-firebase/crashlytics",
[
"expo-build-properties",
{
"ios": {
"useFrameworks": "static"
}
}
]
]
}
}
Listing a module in the Config Plugins (the
"plugins"array in the JSON above) is only required for React Native Firebase modules that involve native installation steps - e.g. modifying the Xcode project,Podfile,build.gradle,AndroidManifest.xmletc. React Native Firebase modules without native steps will work out of the box; no"plugins"entry is required. Not all modules have Expo Config Plugins provided yet. A React Native Firebase module has Config Plugin support if it contains anapp.plugin.jsfile in its package directory (e.g.node_modules/@react-native-firebase/app/app.plugin.js).
Local app compilation
If you are compiling your app locally, run npx expo prebuild --clean to generate the native project directories. Then, follow the local app compilation steps described in Local app development guide in Expo docs. If you prefer using a build service, refer to EAS Build.
Expo Tools for VSCode
If you are using the Expo Tools VSCode extension, the IntelliSense will display a list of available plugins when editing the plugins section of app.json.
Other / Web
If you are using the firebase-js-sdk fallback support for web or "other" platforms then you must initialize Firebase dynamically by calling initializeApp.
However, you only want to do this for the web platform. For non-web / native apps the "default" firebase app instance will already be configured by the native google-services.json / GoogleServices-Info.plist files as mentioned above.
At some point during your application's bootstrap processes, initialize firebase like this:
import { getApp, initializeApp } from '@react-native-firebase/app';
// web requires dynamic initialization on web prior to using firebase
if (Platform.OS === 'web') {
const firebaseConfig = {
// ... config items pasted from firebase console for your web app here
};
initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
}
// ...now throughout your app, use firebase APIs normally, for example:
const firebaseApp = getApp();
Miscellaneous
Android Enabling Multidex
As your application starts to grow with more native dependencies, your builds may start to fail with the common
Execution failed for task ':app:mergeDexDebug' error. This error occurs when Android reaches the
64k methods limit.
One common solution is to enable multidex support for Android. This is a common solution to solving the problem, however it is recommended you read the Android documentation to understand how it may impact your application.
Hermes Support
To support the Hermes JavaScript engine, React Native 0.64.0 or newer is required. However, we cannot guarantee that React Native Firebase works perfectly on it, so please test your project carefully.
Overriding Native SDK Versions
React Native Firebase internally sets the versions of the native SDKs which each module uses. Each release of the library is tested against a fixed set of SDK versions (e.g. Firebase SDKs), allowing us to be confident that every feature the library supports is working as expected.
Sometimes it's required to change these versions to play nicely with other React Native libraries or to work around temporary build failures; therefore we allow manually overriding these native SDK versions.
Using your own SDK versions is not recommended and not supported as it can lead to unexpected build failures when new react-native-firebase versions are released that expect to use new SDK versions. Proceed with caution and remove these overrides as soon as possible when no longer needed.
Android
Within your projects /android/build.gradle file, provide your own versions by specifying any of the following options shown below:
project.ext {
set('react-native', [
versions: [
// Overriding Build/Android SDK Versions
android : [
minSdk : 21, // 23+ if using auth module
targetSdk : 33,
compileSdk: 34,
],
// Overriding Library SDK Versions
firebase: [
// Override Firebase SDK Version
bom : "33.8.0"
],
],
])
}
Once changed, rebuild your application with npx react-native run-android.
iOS
Open your projects /ios/Podfile and add any of the globals shown below to the top of the file:
# Override Firebase SDK Version
$FirebaseSDKVersion = '11.7.0'
Once changed, reinstall your projects pods via pod install and rebuild your project with npx react-native run-ios.
Alternatively, if you cannot edit the Podfile easily (as when using Expo), you may add the environment variable FIREBASE_SDK_VERSION=11.5.0 (or whatever version you need) to the command line that installs pods. For example FIREBASE_SDK_VERSION=11.5.0 yarn expo prebuild --clean
Increasing Android build memory
As you add more Firebase modules, there is an incredible demand placed on the Android build system, and the default memory
settings will not work. To avoid OutOfMemory errors during Android builds, you should uncomment the alternate Gradle memory
setting present in /android/gradle.properties:
# Specifies the JVM arguments used for the daemon process.
# The setting is particularly useful for tweaking memory settings.
# Default value: -Xmx10248m -XX:MaxPermSize=256m
org.gradle.jvmargs=-Xmx2048m -XX:MaxPermSize=512m -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8
Android Performance
On Android, React Native Firebase uses thread pool executor to provide improved performance and managed resources.
To increase throughput, you can tune the thread pool executor via firebase.json file within the root of your project:
// <project-root>/firebase.json
{
"react-native": {
"android_task_executor_maximum_pool_size": 10,
"android_task_executor_keep_alive_seconds": 3
}
}
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
android_task_executor_maximum_pool_size | Maximum pool size of ThreadPoolExecutor. Defaults to 1. Larger values typically improve performance when executing large numbers of asynchronous tasks, e.g. Firestore queries. Setting this value to 0 completely disables the pooled executor and all tasks execute in serial per module. |
android_task_executor_keep_alive_seconds | Keep-alive time of ThreadPoolExecutor, in seconds. Defaults to 3. Excess threads in the pool executor will be terminated if they have been idle for more than the keep-alive time. This value doesn't have any effect when the maximum pool size is lower than 2. |
